When it comes to automating browser actions, developers often ask what is Selenium WebDriver and why it has become the industry standard. Selenium WebDriver is an API that allows your code to directly interact with web browsers, enabling you to simulate user actions such as clicking, typing, navigating, and validating page elements. This connection between code and browser makes it a powerful tool for building reliable test automation frameworks.
Understanding the Browser Architecture
To understand how code interacts with online pages, one must have a solid understanding of the browser architecture. The user interface, rendering engine, JavaScript engine, networking layer, and storage systems are some of the parts that make up a modern browser. The rendering engine builds the DOM and renders the information visually after parsing HTML and CSS when a web page loads.
For concurrent operations, the JavaScript engine simultaneously runs scripts and controls the event loop. Together, these parts manage site modifications, API requests, and user interactions. The developers can write more effective code and connect their functionality with browser behavior by using APIs if they understand this architecture.
An overview of the web API
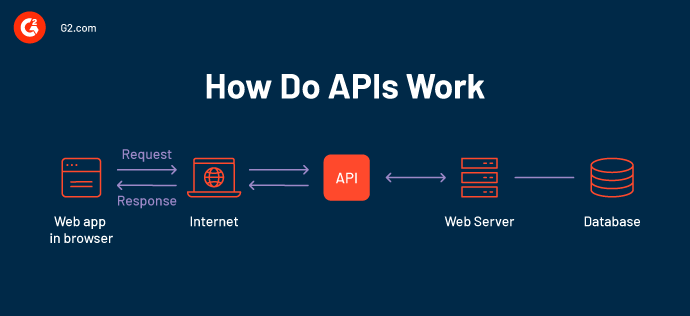
APIs for web browsers are native interfaces that allow developers to use JavaScript to interact with various features and functionalities of the browser. APIs enable developers to use a wide range of functionalities, which go far beyond simple page manipulation. These features include storage, network queries, sensor data, media inputs, and graphics rendering.
By concealing a large portion of the intricacy of the browser’s internal workings behind straightforward method calls, browser APIs enable developers to create dynamic, interactive, and feature-rich web apps. They are essential tools for tying web code to the underlying hardware and browser engine. For example, when learning what is Selenium WebDriver, you’ll see how it builds on these browser APIs to provide a unified way to automate and control browsers. Similarly, modern approaches like using an AI agent for QA testing extend these capabilities further by enabling intelligent test execution, analysis, and optimization.
Features of the Web browser API
With web browser APIs, developers can access a browser environment and add features to web apps. These APIs make difficult tasks much more straightforward by providing simple JavaScript functions. This also handles complex operations, including device contacts and hardware, communications with outside services, and modifications to website content.
Here are some important aspects of web browser APIs:
- Manipulating the DOM: Without requiring a page reload, it allows developers to alter an existing website’s structure, layout, and content. The ability to modify a webpage simply involves reacting to user interaction or a change in data using APIs like document.querySelector() and element.innerHTML. In comparison, when you study what is Selenium WebDriver, you’ll see how it uses these DOM interactions programmatically for automated browser testing.
- Async networking: It explores the web UI to be able to connect to servers without needing a page refresh. APIs such as Fetch and XMLHttpRequest allow us to build modern single-page applications (SPAs), use AJAX requests, or just have real-time updates.
- Access to devices and sensors: APIs allow access to specific device data and features (Geolocation, Battery Status, Vibration). With these, applications can access location data, which leads to location-based services software that enhances mobile experiences.
- Visuals and motion design: Tools like Canvas, WebGL, and SVG make rendering 2D and 3D graphics much easier. All things visualizations, games, and interactivity depend on these.
- Performance monitoring: To improve user experience and spot bottlenecks, the Performance and Navigation Timing APIs assist in monitoring load times, resource usage, and other metrics. Modern approaches, like an AI agent for QA testing, take these insights further by analyzing performance data intelligently and helping testers focus on the most critical issues.
Significance of understanding web browser APIs
The web browser application programming interfaces, or APIs, are at the heart of modern web development. They provide developers with the ability to develop interactive, dynamic, and highly functional applications. Understanding these APIs is also foundational when exploring what is Selenium WebDriver, as WebDriver relies on these browser-level interactions to automate and test web applications effectively.
The following are some important reasons for developing a general understanding of browser APIs:
- Improves engagement in applications: Learning how to use APIs like the DOM and Event APIs lets developers respond to users immediately, producing a smooth user experience with fast response and dynamic content updates.
- Facilitates effective data management: Fetch, localStorage, and IndexedDB are APIs that provide simpler processes for transferring data between client and server, and storing data on the device, improving responsiveness. Leveraging an AI agent for QA testing can further analyze these interactions automatically to ensure data flows are tested efficiently.
- Enhances compatibility across browsers: A thorough understanding of standardized APIs guarantees that their functions will work consistently across a wide range of browsers and scenarios, reducing errors and compatibility problems.
- Facilitates responsive and adaptive layouts: APIs such as Media Queries, Screen, and Orientation APIs help provide better usability, functionality, and accessibility by allowing developers to adapt programs to different devices, multiple screen sizes, and configurations.
Different types of Web browser APIs
APIs for web browsers are classified according to the features they offer to developers. These APIs give developers a defined way to interact with the browser and system resources so they can develop responsive and dynamic web apps. Understanding these APIs is also essential when learning what is Selenium WebDriver, as WebDriver leverages these browser-level interactions to automate testing effectively.
The types of web browser APIs are listed below with descriptions of each one:
- Document Object Model (DOM) APIs
The structure and content of a web page are represented by a hierarchy of objects created using the DOM. Developers can find, access, and manipulate any node using methods like querySelector and getElementById. The DOM is central for building dynamic web applications with real-time responsiveness, which is crucial when performing testing with AI to validate interactive features automatically. - API for Device and Sensor
APIs enable web apps to work with hardware features like Geolocation, Vibration, Battery Status, Ambient Light, and more. This is especially valuable for mobile and IoT web apps, where an AI agent for QA testing can help simulate and validate device-specific behavior efficiently. - Browser Object Model (BOM) APIs
The web browser has objects called the BOM. These allow developers to interact with browser-specific features beyond page content, including window, navigator, screen, location, and history objects. The BOM enhances user experience and is something Selenium WebDriver interacts with during automated browser tests. - APIs for User Interfaces
Compute APIs manage interactions beyond standard user input, such as system notifications, clipboard data, or full-screen mode. Examples include the Fullscreen API, Clipboard API, and Notifications API. These UI interactions can also be verified efficiently using testing with AI to ensure consistent behavior. - Performance and Timing APIs
Performance and timing APIs (Performance API, User Timing API, Resource Timing API) allow measurement of load times, resource usage, and app performance, data that is useful for AI testing frameworks to detect bottlenecks or performance issues. - APIs for Credential Management and Security
APIs like the Credential Management API and Permissions API help manage secure logins and restrict access to sensitive components such as the camera, microphone, and geolocation. An AI agent for QA testing can help automate verification of these security features across multiple devices and browsers.
How do Web APIs interact with the browser environment during testing?
Web APIs play an essential role in how browsers respond to automated testing scripts, especially when implemented in cloud environments across different browsers and devices. Web APIs enable test frameworks to replicate user activities, validate user interface elements, and monitor system reactions. This involves interacting with the browser environment through the exposure of components such as the DOM, network behavior, and storage methods using a cloud-based platform such as LambdaTest that allows you to perform AI testing.
LambdaTest KaneAI is a GenAI-Native AI agent for QA testing that allows teams to plan, author, and evolve tests using natural language. It is built from the ground up for high-speed quality engineering teams and integrates seamlessly with the rest of LambdaTest’s offerings around test planning, execution, orchestration, and analysis.
KaneAI Key Features:
- Intelligent Test Generation: Effortless test creation and evolution through Natural Language (NLP) based instructions.
- Intelligent Test Planner: Automatically generate and automate test steps using high-level objectives.
- Multi-Language Code Export: Convert your automated tests into all major languages and frameworks.
- Sophisticated Testing Capabilities: Express sophisticated conditionals and assertions in natural language.
- API Testing Support: Effortlessly test backends and achieve comprehensive coverage by complementing existing UI tests.
- Increased Device Coverage: Execute your generated tests across 3000+ browsers, OS, and device combinations.
Teams can validate browser behavior in an organized and scalable manner by integrating JUnit testing with their test suites. Using WebDriver or DevTools Protocol, LambdaTest communicates with the browser while it is running, accessing Web APIs to retrieve information, identify events, and confirm conditions.
Whether checking UI functionality or performing regression tests on various browsers and devices, cloud-driven automation through LambdaTest KaneAI as an AI agent for QA testing, combined with JUnit, guarantees strong, efficient, and scalable quality assurance for modern web applications.
Security Implications of Web APIs
Web browser APIs provide useful features to provide a better user experience and enhanced interactivity, but they may also create security and privacy risks. The APIs mostly provide access at the browser level, and in some cases at the system level. The following are the primary security factors to be taken into account when using web browser APIs:
- Same-origin policy (SOP): The Same-Origin Policy prevents a software program or document from a single source from interacting with an additional program or document from another source. It does this by stopping harmful scripts from obtaining private data across domains, which is a key security feature.
- Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS): Control access to resources outside of the origin of a web page is possible with CORS policies. An incorrectly configured CORS setting may enable hackers from unauthorized domain names to access APIs and risk the security of your information.
- APIs based on permissions: APIs like Geolocation, Notifications, and Clipboard APIs demand an explicit act of user consent; users may not have sufficient consent or understanding of the APIs if there is a lack, or if there is enough consent that encourages the use of APIs to surveil users or collect personal information potentially.
- Cross-origin scripting (XSS): When information about users has not been properly purified, DOM-manipulating APIs may introduce malicious scripts, which could result in loss of information, session hijacking, or website trespassing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the APIs that allow the code you write to interact with a web browser is essential for creating modern and innovative, appealing, and secure online apps. From using the DOM to more complex browser-based automation, the Web APIs are at the core of web development. As browser functionality improves, understanding these interfaces will always lead to a more informed developer creating smooth, powerful experiences that harness the potential of the web.